Introduction
Over the last decade, the way people work has undergone a massive transformation. One of the most disruptive shifts has been the rise of the gig economy — a labor market defined by short-term contracts, freelance projects, and on-demand jobs.
What Is the Gig Economy?
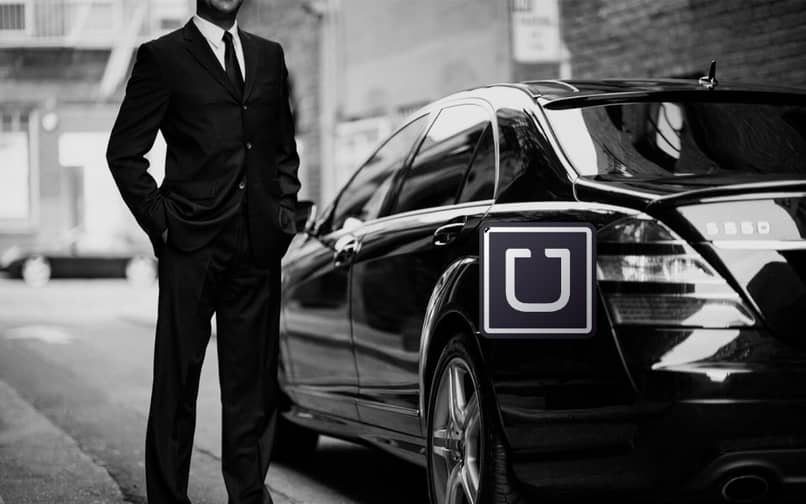
The gig economy refers to a flexible job market where individuals work as independent contractors rather than full-time employees. This includes Uber drivers, freelance designers, delivery workers, software developers, consultants, and more.
Fueled by platforms like Upwork, DoorDash, and Fiverr, the gig economy offers workers greater flexibility while enabling businesses to scale more efficiently.
Why Is It Growing?
Several factors contribute to its rapid expansion:
- Technology: Apps and platforms make it easy to find and manage gig work.
- Flexibility: Many workers prioritize autonomy and remote options.
- Economic shifts: Companies are reducing overhead by hiring contractors instead of full-time staff.
According to some estimates, over 35% of U.S. workers are now engaged in some form of gig or freelance work.
The Pros and Cons
Pros for Workers:
- Flexible hours and remote work
- Diverse income sources
- Entrepreneurial freedom
Cons:
- Lack of benefits (healthcare, retirement)
- Income instability
- Fewer legal protections
For businesses, the gig economy offers agile labor at reduced cost, but it also raises challenges around worker loyalty, quality control, and ethics.
What Does the Future Hold?
The gig economy is unlikely to fade. If anything, it’s becoming a core component of the labor market. Governments and platforms will need to adapt with new policies and protections to ensure fair treatment without sacrificing flexibility.
Conclusion
The gig economy is redefining what it means to work in the 21st century. While it presents opportunities for freedom and innovation, it also demands serious attention to issues of equity, security, and sustainability.
What’s your take? Are you thriving in the gig world or cautious about its rise?